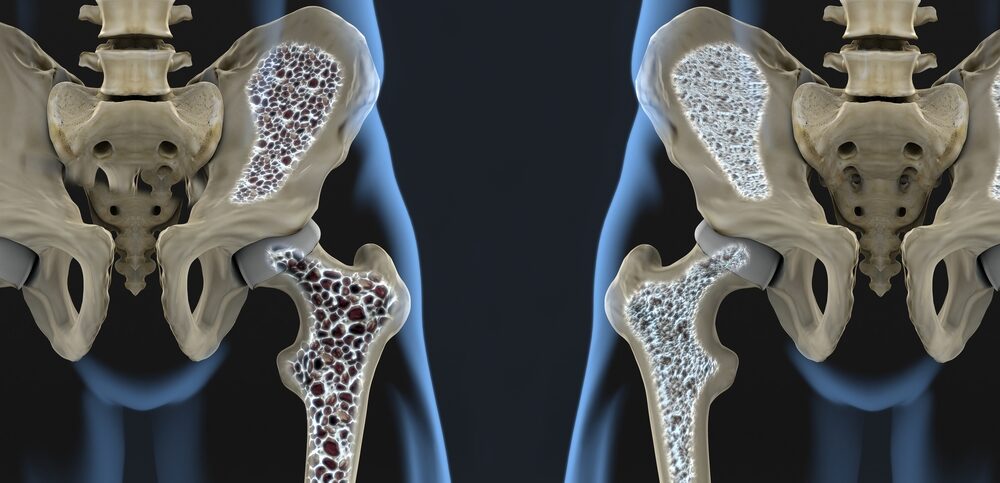
Did you know that approximately 54 million Americans have osteoporosis or low bone mass, putting them at increased risk for fractures? Osteoporosis is a significant concern as it affects bone health, making prevention and management strategies crucial for maintaining a strong skeletal system.
At Orthopedic Specialists of SW Florida, we are dedicated to providing exceptional care for patients with musculoskeletal needs. Our expert team understands the complexities of osteoporosis and offers personalized assessments to develop effective prevention and management plans tailored to you. Schedule an appointment with us today to take proactive steps towards better bone health.
In this blog, we will delve deeper into osteoporosis, its impact on bone health, and the importance of adopting effective strategies to combat this condition.
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a bone disease marked by weakened bone tissue, leading to an increased risk of fractures. This condition occurs when the body loses bone mass more quickly than in can produce new bone, often progressing silently without symptoms. Many individuals remain unaware of their declining bone density until a fracture occurs.
Osteoporosis affects both men and women, but it is especially common among postmenopausal women due to a drop in estrogen levels, which are crucial for maintaining bone density. According to the National Osteoporosis Foundation, about 1 in 2 women and 1 in 4 men aged 50 or older will experience a fracture related to osteoporosis in their lifetime. Certain groups, including those over 65, individuals with a family history of the disease, and specific ethnicities like Caucasians and Asians, are at a greater risk.
Bone density is a key factor in understanding osteoporosis, as it measures the amount of minerals, such as calcium, in your bones. A higher bone mineral density (BMD) indicates stronger bones, while a lower BMD means weaker bones that are more susceptible to fractures. Regular screening, including bone density tests, is essential for early detection and effective management of osteoporosis, particularly for those at increased risk.
Causes of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can be attributed to a variety of factors, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Decreased levels of hormones, particularly estrogen in women during menopause and testosterone in men, contribute significantly to bone loss.
- Genetics: A family history of osteoporosis can increase an individual’s risk, as genetics play a vital role in bone density and skeletal health.
- Age: As people age, bone resorption (the process of bone breakdown) tends to outpace bone formation, leading to a gradual reduction in bone density.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Insufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D can hinder the body’s ability to build and maintain strong bones.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises, prevents the bones from experiencing the stresses needed for optimal growth.
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect bone health by interfering with the body’s ability to absorb calcium and generate new bone tissue.
- Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, such as rheumatoid arthritis, malabsorption syndromes, and chronic kidney disease, can contribute to weakened bones.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can lead to diminished bone density over time.
Understanding the causes of osteoporosis is crucial for effective prevention and management. Key factors include hormonal changes, genetics, age, and nutritional deficiencies, as well as a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, pre-existing medical conditions and long-term use of certain medications can exacerbate bone loss, increasing the risk of fractures. Addressing these issues through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions is essential for maintaining bone health and reducing fracture risks.
Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors associated with osteoporosis is crucial for effective prevention and management. By identifying individuals at higher risk, tailored interventions and proactive measures can be implemented to maintain bone health. This section explores the various intrinsic and extrinsic factors contributing to the likelihood of developing osteoporosis, highlighting how lifestyle choices and genetic predispositions can influence bone density over time, as well as their relationship to conditions like breast cancer and the risk of hip fractures.
Intrinsic Risk Factors
- Age: Bone density typically declines with age, especially in individuals over 50.
- Sex: Women are at higher risk due to postmenopausal hormonal changes that accelerate bone loss.
- Family History: Genetics play a significant role in bone density and skeletal health. Those with a family history of osteoporosis or related fractures are more likely to experience similar issues.
Extrinsic Risk Factors
- Sedentary Lifestyle: A lack of physical activity can weakens bones. Incorporating weight-bearing and resistance exercises is vital for bone health.
- Nutrition: Diets low in calcium and vitamin D can impede bone strength and density.
- Medication Use: Long-term use of corticosteroids and other medications can adversely affect bone health; patients should discuss these risks with their healthcare provider.
Identifying personal risk factors for osteoporosis is essential for early intervention and effective management. Understanding these factors allows individuals to make proactive lifestyle changes and undergo regular bone density screenings. Early detection can lead to timely treatments that can slow bone loss and reduce fracture risk, including hip fractures, empowering individuals to make informed health decisions.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing osteoporosis and managing its effects require a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle changes and medical interventions. The focus on prevention and treatment can help reduce the risk of fractures and maintain bone health throughout life, highlighting the importance of early detection and proactive measures.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health. Calcium helps build and maintain bone density, while vitamin D enhances calcium absorption. Incorporate dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods into your diet, and consider supplements if needed.
- Regular Weight-Bearing Exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, dancing, and resistance training, helps to build and maintain bone density. These activities stimulate bone growth and strengthen muscles, which can improve balance and reduce the risk of falls.
- Strength Training: Incorporating strength training into your routine is vital for building muscle mass and enhancing bone strength. Exercises using free weights, resistance bands, or body weight help improve overall strength, coordination, and stability, which are crucial for preventing osteoporosis.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are critical for bone health. Smoking has been linked to decreased bone density, and excessive alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Bone Health Screening: Regular screenings, particularly for individuals at higher risk, can help detect early signs of bone density loss. Bone density tests can provide valuable information for preventive measures and allow for timely intervention.
- Nutrition and Dietary Habits: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support overall health, including bone health. Nutrients like magnesium, potassium, and vitamin K also play essential roles in bone maintenance.
- Medication Management: If you are on medications that may contribute to bone loss, such as long-term corticosteroids, discuss alternative options with your healthcare provider. They can help you find ways to manage your health without compromising bone density.
- Fall Prevention Strategies: Taking steps to prevent falls, such as improving home safety (removing tripping hazards, using non-slip mats), ensuring good lighting, and wearing appropriate footwear, can significantly reduce the risk of fractures and injuries related to osteoporosis.
By adopting these prevention strategies, individuals can proactively reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis and bone fractures, while promoting better bone health throughout their lives.
Management Options
Effectively managing osteoporosis requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses both medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. By understanding the available options, individuals can work closely with healthcare providers to create tailored plans that address their specific needs and improve overall bone health.
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Participating in personalized physical therapy sessions can greatly enhance mobility, strength, and balance, which are vital for effectively managing low bone density and osteoporosis.
- Medications: There are various medications available to treat osteoporosis, including bisphosphonates, hormone replacement therapy, and selective estrogen receptor modulators, all of which can help strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk.
- Exercise Programs: Implementing structured exercise regimens that emphasize weight-bearing and resistance training can boost bone density and improve overall physical function.
- Education and Counseling: Gaining knowledge about osteoporosis through educational workshops and counseling empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health and treatment options.
- Regular Monitoring: Consistent follow-ups and bone density screenings are essential for tracking the progression of osteoporosis and assessing the effectiveness of the treatment plan, enabling timely adjustments as necessary.
- Support Groups: Joining osteoporosis support groups can offer emotional support, motivation, and the sharing of experiences among individuals facing similar challenges.
Prioritize Your Bone Health Today
Early detection and proactive management are crucial for maintaining strong bones, especially for those at risk of severe osteoporosis. At Orthopedic Specialists of SW Florida, we’re dedicated to helping you achieve optimal bone health.
Don’t hesitate—schedule an appointment with us today to discuss your bone health and discover our specialized services!